Core Concepts
Before you start using ByteEngine, it helps to understand the core building blocks of the platform. Each one solves a unique healthcare AI challenge — but together, they form the foundation of your intelligent system.
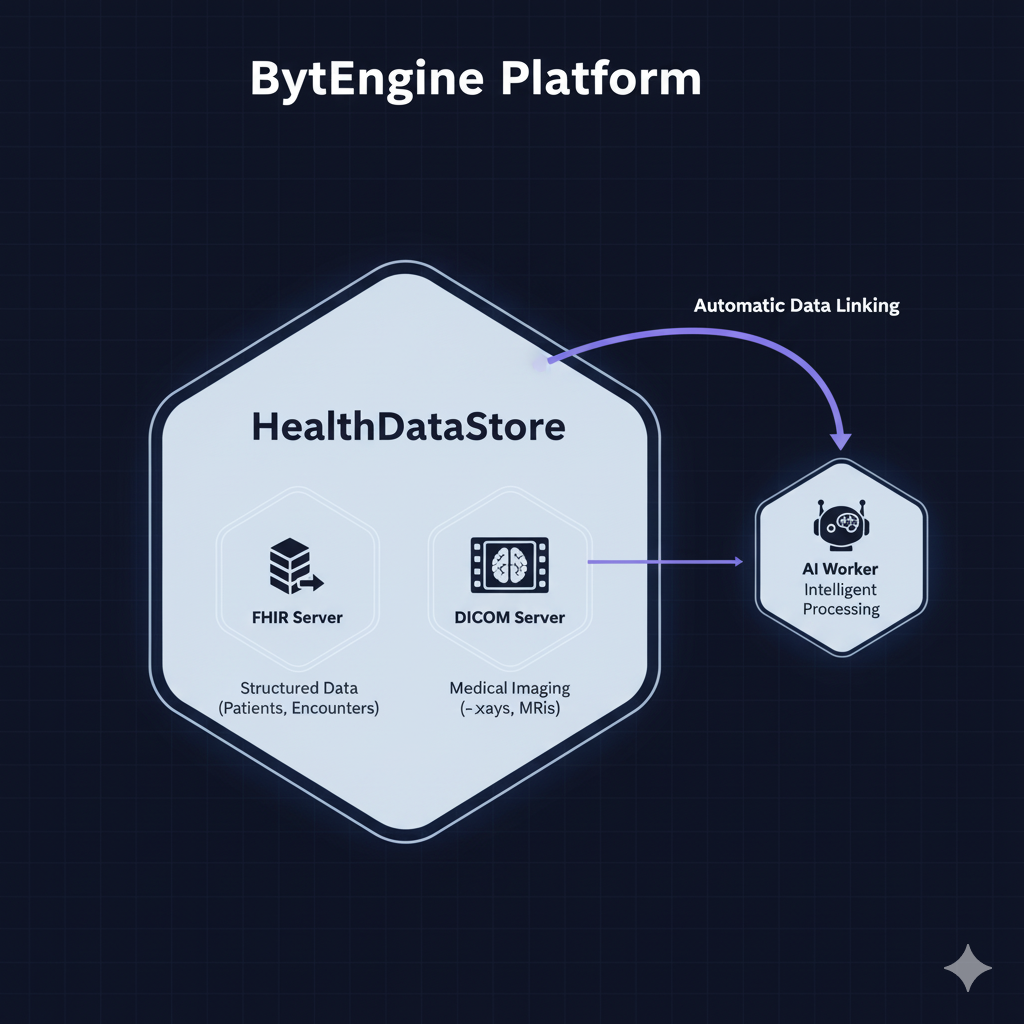
HealthDataStore
What It Is
Your digital health data warehouse. ByteEngine's HealthDataStore lets you create and manage:
- FHIR servers for structured health data (patients, observations, encounters, etc.)
- DICOM servers for medical imaging (X-rays, MRIs, etc.)
All with built-in data residency, security, and interoperability.
Real-World Example
Imagine a telemedicine startup that needs to store patient records and images:
- They create a FHIR server for patient and encounter data.
- They create a DICOM server for imaging studies.
- The AI Worker automatically links a patient's X-ray with their visit summary.
Example Setup
import { EngineClient } from '@boolbyte/engine';
const client = new EngineClient({ apiKey: 'YOUR_API_KEY' });
const healthStore = await client.dataStore.createFhirStore({
name: 'telemed-fhir',
region: 'global',
fhirVersion: 'R4',
type: 'serverless'
});
You'll instantly receive credentials and an endpoint like:
https://api.engine.boolbyte.com/fhir/telemed-fhir
→ FHIR API Reference | → DICOM API Reference
Visual Overview
AI Workers
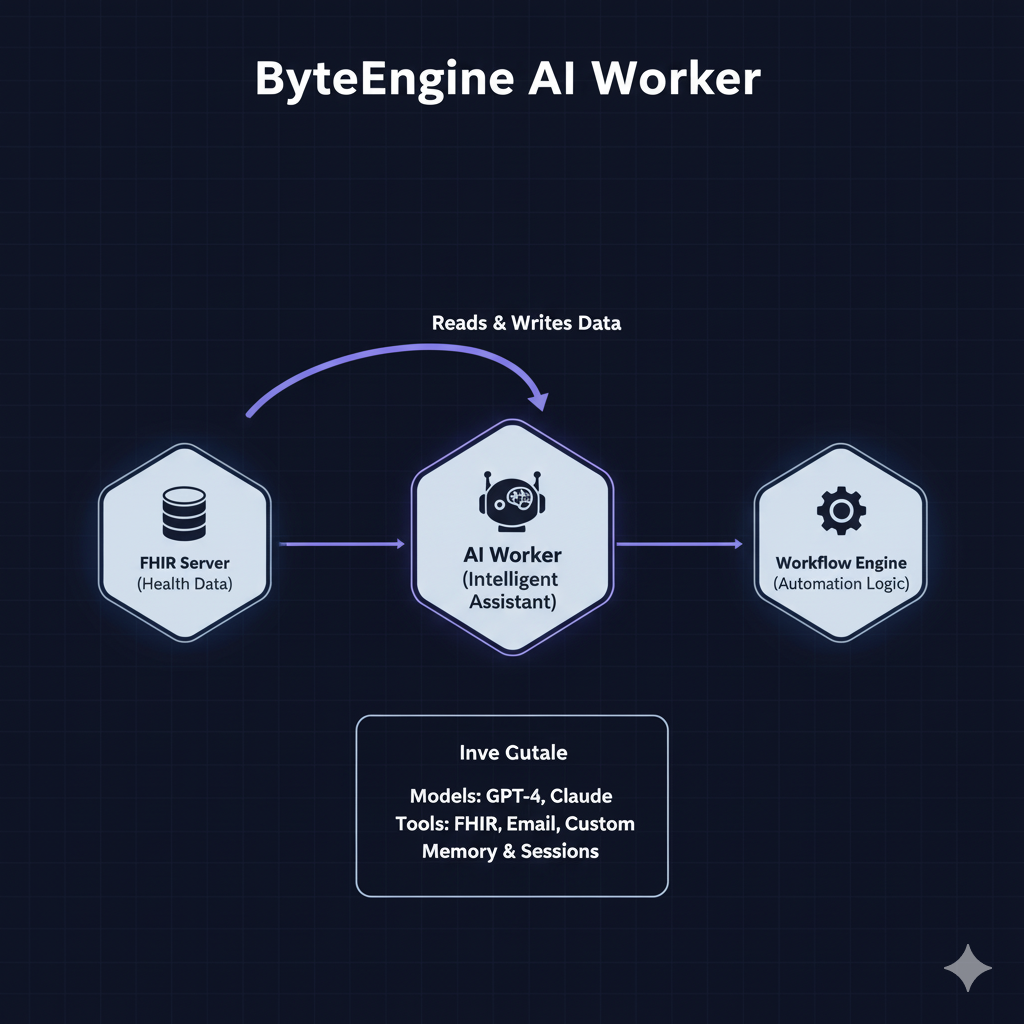
What They Are
AI Workers are your intelligent assistants inside ByteEngine. They think, reason, and act — using AI models like GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, or medical-specific models like MedGemma-27b.
Each worker can:
- Access your FHIR or DICOM servers
- Perform function calls and tool executions
- Operate in loops or workflows
- Retain memory through Sessions
Analogy
Think of them like virtual healthcare assistants who can read medical data, reason over it, and then take an action — such as summarizing, analyzing, or triggering alerts.
Example Use Case
A "LabResultsWorker" that:
- Listens for new lab results in your FHIR server
- Detects abnormal values (like high glucose)
- Writes a note or sends an alert to the clinician
Example Setup
const worker = await client.worker.createWorker({
name: 'LabResultsWorker',
defaultModelName: 'medgemma-27b', // Healthcare model for clinical analysis
instructions: 'You are a healthcare AI assistant specialized in lab result analysis.',
toolConfigs: {
tools: [
{
toolName: 'fhir_access',
config: { serverId: healthStore.data.id }
}
]
}
});
Then, assign the worker to a workflow that triggers it when lab data updates.
Visual Overview
Sessions
What They Are
Sessions manage context and state for your AI workers. They allow ByteEngine to "remember" past interactions, messages, or data states between runs — like an ongoing chat thread or patient case.
Real-World Example
A doctor consults an AI scribe worker during a 20-minute visit.
- The worker remembers each part of the discussion within the same session.
- At the end, it generates a full summary, including all previous steps.
Example Setup
const session = await client.session.createSession({
workerId: worker.data.id,
metadata: {
patientId: '12345'
}
});
Add messages or tasks within that session to build context.
Knowledge Bases
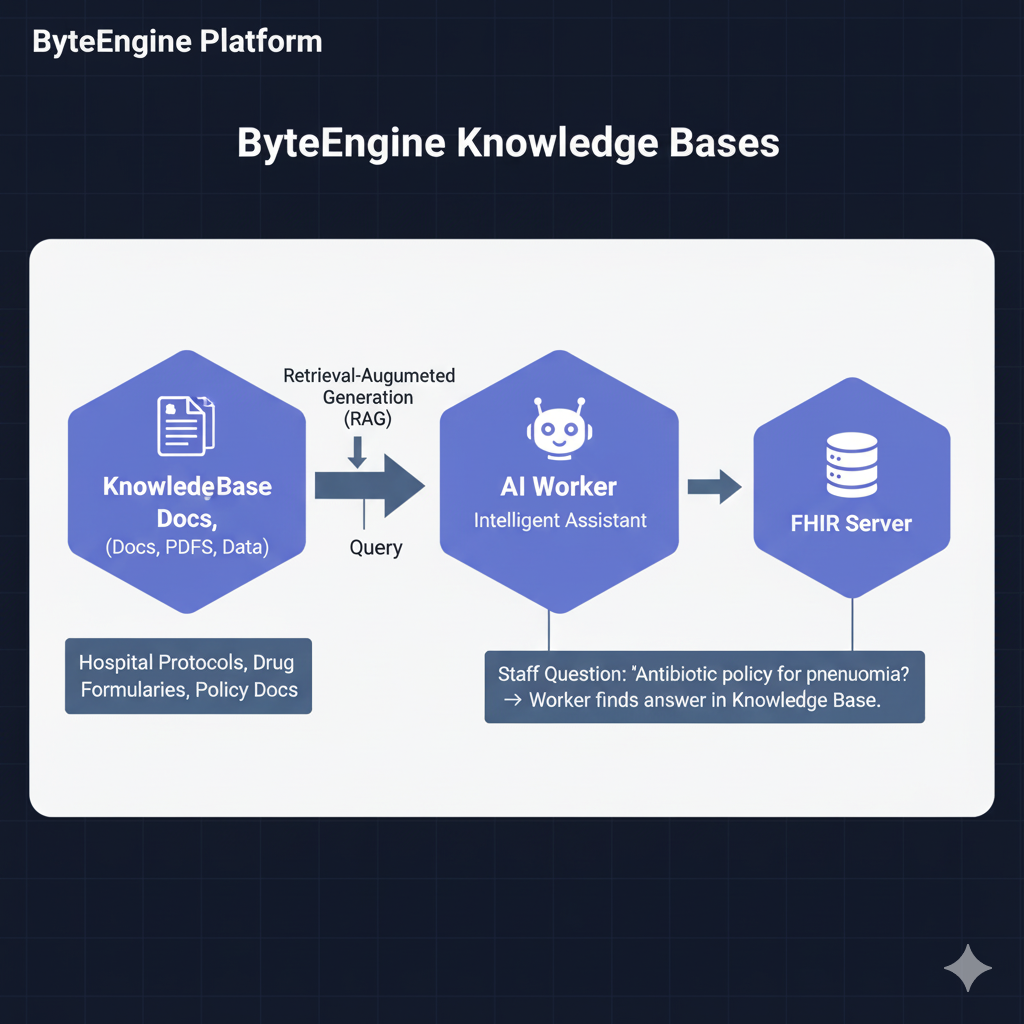
What It Is
A Knowledge Base is your AI's private library. You can upload documents, PDFs, or datasets — ByteEngine automatically indexes and vectorizes them so your AI Workers can search, reference, and reason over that information.
Why It Matters
AI Workers are powerful, but they only know what they've been trained on. Knowledge Bases let you extend their "memory" with your own data — research papers, clinical guidelines, policies, or institutional notes.
Real-World Example
A hospital uploads:
- Treatment protocols
- Local drug formularies
- Policy documents
Their AI Worker can now answer staff questions such as:
"What's our hospital's antibiotic policy for pneumonia?"
and it retrieves the correct answer from the Knowledge Base.
Example Setup
// Create knowledge base
const knowledgeBase = await client.knowledgeBase.createKnowledgeBase({
name: 'HospitalGuidelines',
description: 'Hospital treatment protocols and guidelines',
type: 'text'
});
// Upload a document
const fileKB = await client.knowledgeBase.createKnowledgeBaseFromFile(
pneumoniaGuidelineFile,
'Pneumonia Guidelines',
'Hospital antibiotic policy for pneumonia treatment'
);
→ Knowledge Base API Reference
Visual Overview
File Storage
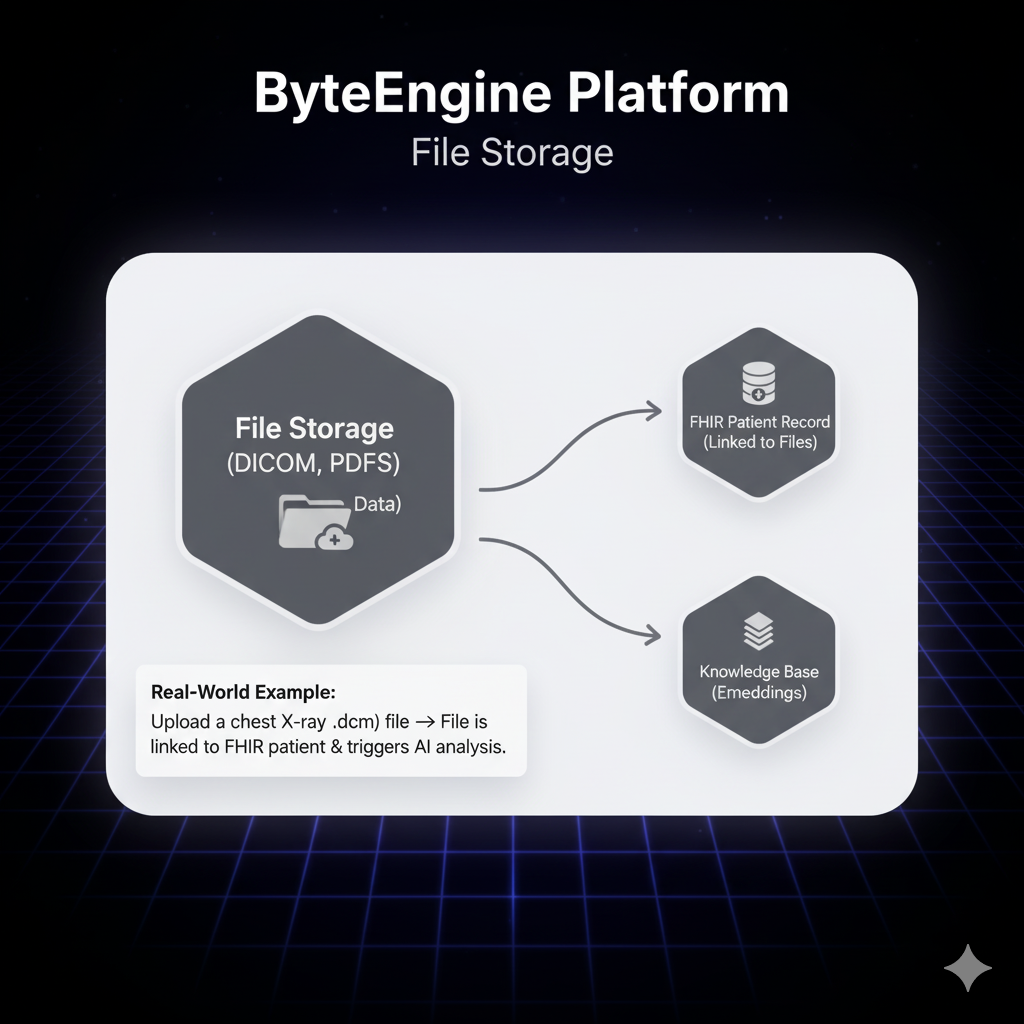
What It Is
Secure, HIPAA-compliant storage for all your medical files — from PDFs to DICOM images. Files stored here can be linked to FHIR resources, Knowledge Bases, or used directly by AI Workers.
Example Use Case
A diagnostic center uploads new imaging studies. A DICOM file triggers an AI Worker to generate a preliminary radiology report.
Example Setup
const storage = await client.storage.createStorage({
name: 'diagnostic-images',
description: 'Storage for diagnostic imaging files'
});
// Upload file with metadata
const file = await client.storage.uploadFile(
chestXrayFile,
{
name: 'chest_xray.dcm',
metadata: { patientId: '12345' }
}
);
You'll get a file ID to use inside workflows.
Visual Overview
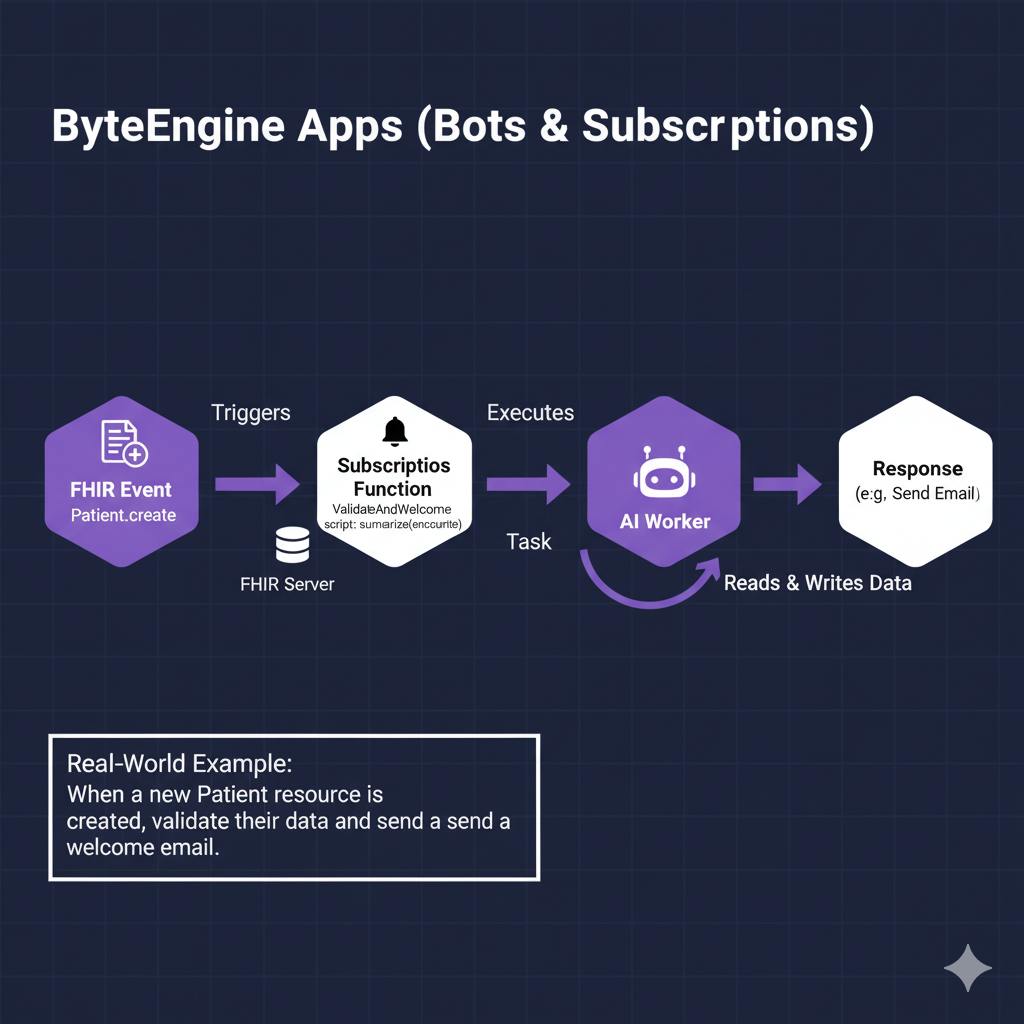
Apps (Bots & Subscriptions)
Bots
Bots are short-lived functions that run code or AI tasks on demand — similar to AWS Lambda.
Use Case: A bot summarizes a patient's visit note whenever a new Encounter resource is created.
// Note: Bot API endpoints would be implemented based on actual API structure
const bot = await client.bot.createBot({
name: 'NoteSummarizer',
trigger: 'manual',
script: 'summarize(encounter)'
});
// Run it
const result = await client.bot.runBot('NoteSummarizer', {
encounterId: 'E123'
});
Subscriptions
Subscriptions are event-based bots. They listen for FHIR events (e.g., a new Patient or Observation) and trigger automatically.
Example: "When a new Patient resource is created, validate their data and send a welcome email."
const subscription = await client.subscription.createSubscription({
event: 'Patient.create',
bot: 'ValidateAndWelcome'
});
→ Bots API Reference | → Subscriptions API Reference
Visual Overview
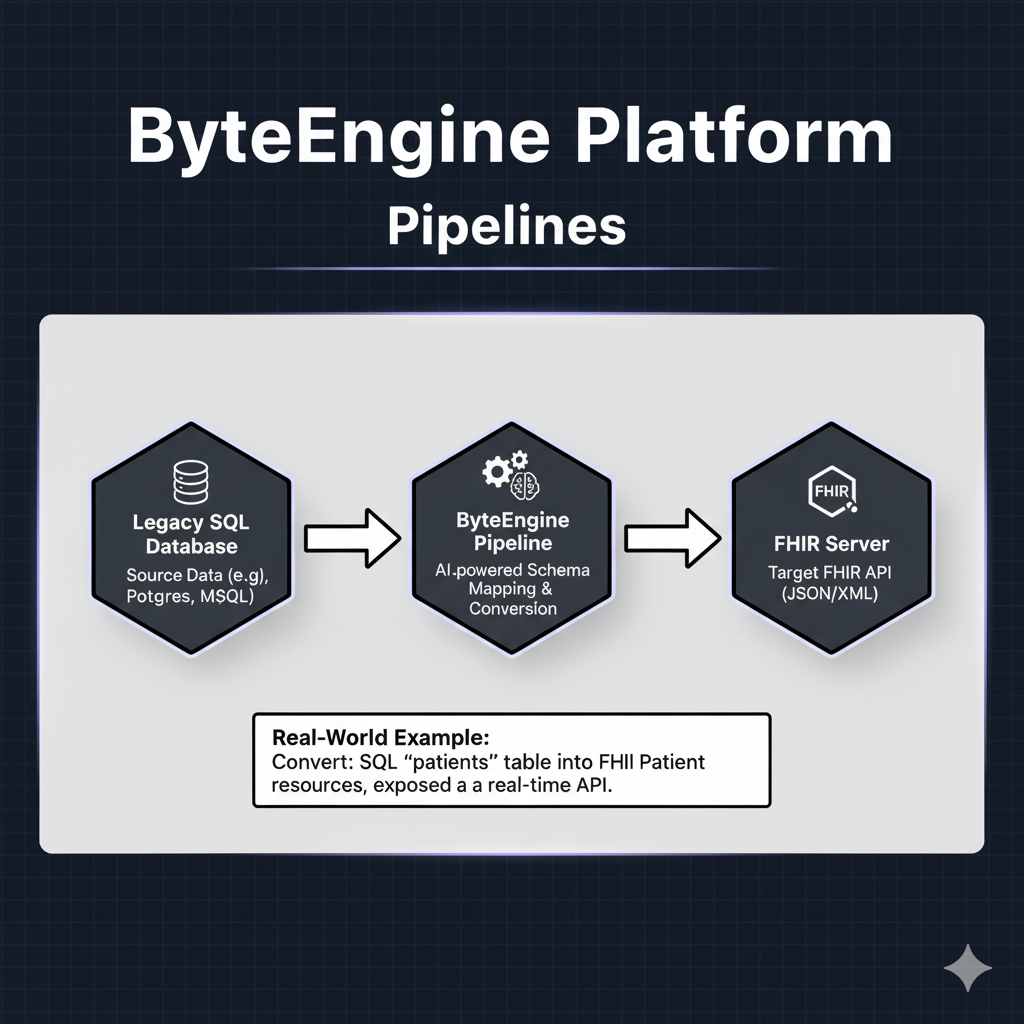
Pipelines
What It Is
Pipelines connect your legacy data systems to FHIR APIs. You simply give ByteEngine a schema or database connection, and it uses AI to automatically map it to FHIR resources.
Why It Matters
Most hospitals and clinics still run on old databases. Pipelines let you expose them as FHIR APIs instantly — no manual data migration needed.
Real-World Example
A hospital with a SQL Server database wants to integrate with FHIR. They create a Pipeline that converts each patients table row into a FHIR Patient resource.
Example Setup
const pipeline = await client.pipeline.createPipeline({
name: 'LegacyToFHIR',
source: {
type: 'postgres',
connection: 'postgres://user:pass@db/patientdb'
},
target: {
type: 'fhir',
server: 'telemed-fhir'
}
});
Once deployed, calling the pipeline endpoint returns FHIR-formatted data.
Visual Overview
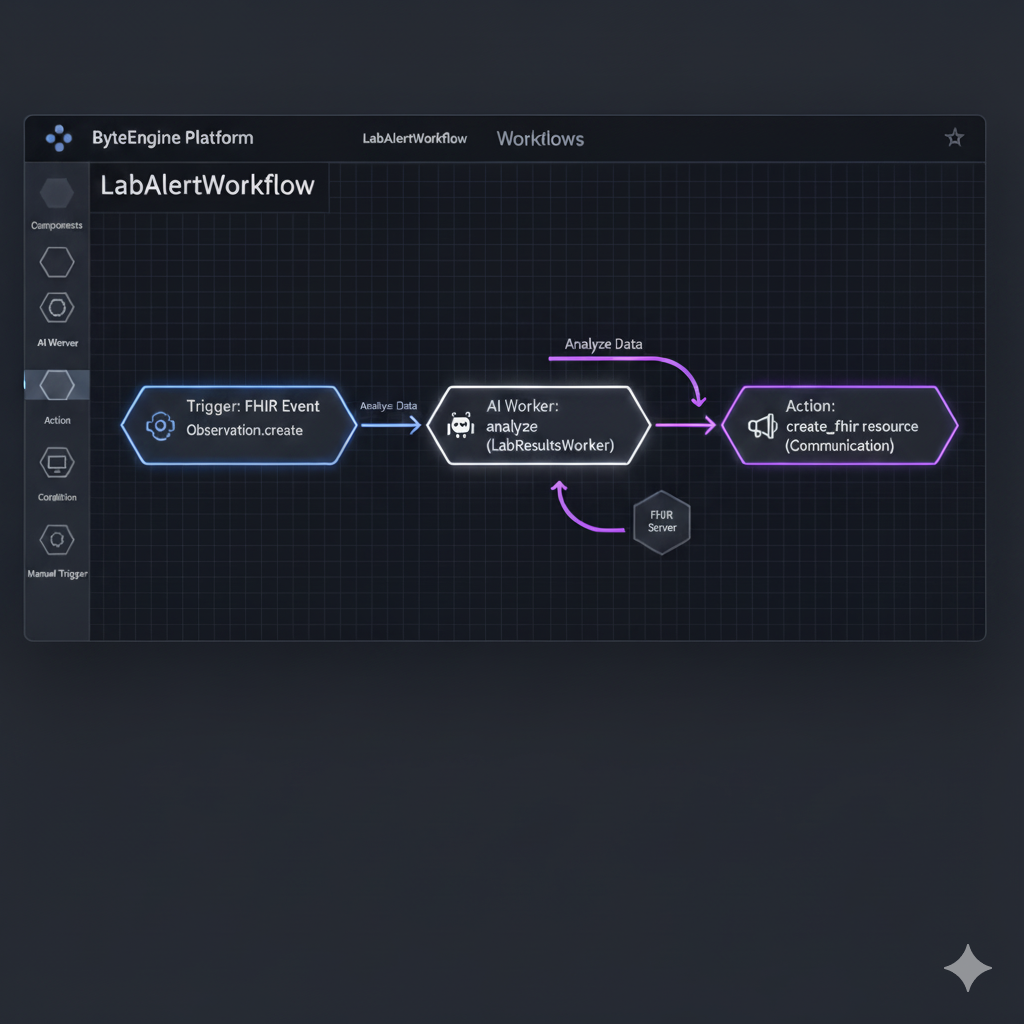
Workflows
What It Is
Workflows are the heart of ByteEngine — they let you orchestrate data, AI Workers, pipelines, and bots into intelligent, automated flows.
You can build them using:
- The Visual Workflow Builder (drag-and-drop interface) or
- YAML/JSON configuration files
Example Use Case
A "Lab Alert" workflow:
- A new Observation (lab result) arrives.
- The AI Worker analyzes it.
- If values are abnormal, it creates a FHIR Communication resource to notify the clinician.
Example YAML Config
name: LabAlertWorkflow
trigger:
event: Observation.create
steps:
- name: analyze
worker: LabResultsWorker
- name: notify
action: create_fhir_resource
resource_type: Communication
input:
message: "Abnormal result detected for {{patient_id}}"
Deploy it:
const workflow = await client.workflow.deployWorkflow({
name: 'LabAlertWorkflow',
config: workflowYaml
});
Visual Overview
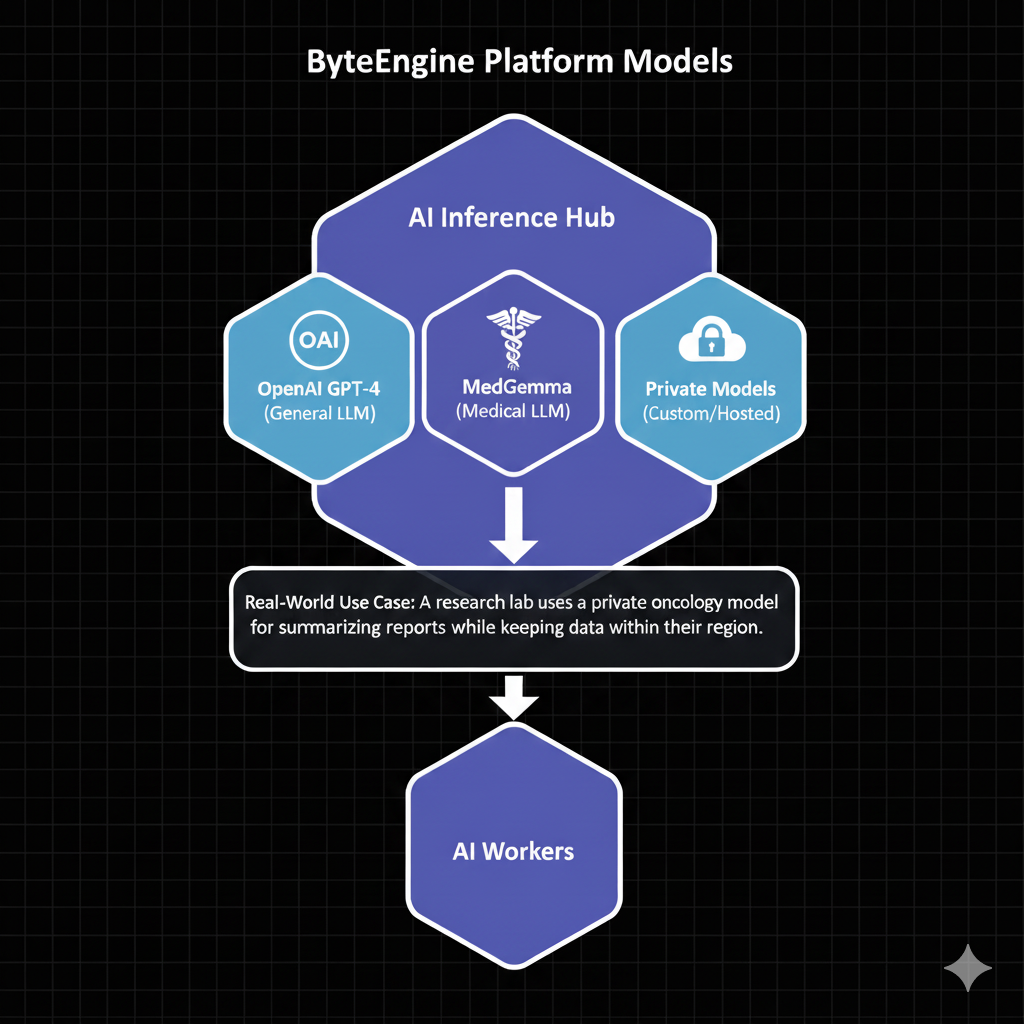
Models
What It Is
The Models service is your AI inference hub. It gives you a single interface to run and manage AI models — from general purpose LLMs to healthcare-specific models.
Supported Model Types
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| General LLMs | OpenAI GPT-4, Anthropic Claude 3, GPT-OSS-120b |
| Medical Models | MedGemma-27b, LinkShare Medical, Mayo MedLM |
| Private Models | Your own hosted models for internal use |
Example Use Case
A research lab uses a private oncology model for summarizing tumor board reports while keeping data within their region.
Example Setup
// List available models
const models = await client.model.getModels();
// Create worker with specific model
const oncologyWorker = await client.worker.createWorker({
name: 'oncology-summarizer',
defaultModelName: 'medgemma-27b', // Healthcare model for medical analysis
instructions: 'You are a specialized oncology AI assistant for tumor board reports.'
});
Visual Overview
Next Steps
Now that you understand the core concepts, try the Quick Start Guide to see them in action.